PDF Converter: It’s everywhere, right? From converting that killer essay for your prof to turning your scanned lecture notes into searchable text, PDF converters are total lifesavers. But have you ever wondered about the tech behind them? This deep dive explores the PDF converter market, from the big players and different types of converters (online, desktop, mobile – you name it!) to the security concerns and future trends.
We’ll also check out the user experience, pricing models, and how these tools integrate with other apps. Get ready to become a PDF conversion guru!
We’ll unpack the nitty-gritty details of how PDF converters work, including different conversion methods (OCR, image-based, text-based), the potential for formatting loss, and best practices for keeping your sensitive documents safe. We’ll even look at the user interfaces of popular converters and explore what makes for a truly awesome user experience. Plus, we’ll touch on accessibility features and future tech advancements in the field.
Basically, everything you ever wanted to know about PDF converters (and probably more).
PDF Converter Market Overview
The PDF converter market is a bustling landscape, constantly evolving with new technologies and user demands. It’s a market driven by the ubiquitous nature of PDF files across personal and professional settings, necessitating tools for conversion, editing, and management. The increasing reliance on digital documents and the need for seamless cross-platform compatibility fuel its ongoing growth.
Major Players in the PDF Converter Market
Several key players dominate the PDF converter market, each offering a range of features and pricing models. Adobe Acrobat, a long-standing industry leader, remains a prominent force, known for its comprehensive suite of PDF tools. However, numerous competitors offer compelling alternatives, catering to various user needs and budgets. These include smaller companies specializing in specific functionalities, as well as larger tech corporations integrating PDF capabilities into their broader software ecosystems.
Examples of such competitors include Nitro PDF, Smallpdf, and Foxit PDF Editor. The competitive landscape is characterized by continuous innovation and a focus on user experience.
Types of PDF Converters
The PDF converter market offers a variety of options to suit different user preferences and technical capabilities. Online converters provide a readily accessible, browser-based solution, ideal for occasional use and simple conversions. Desktop applications, conversely, offer more advanced features and often integrate more seamlessly with existing workflows. These usually require installation and offer more power and features. Mobile apps bring the convenience of PDF conversion directly to smartphones and tablets, enabling on-the-go document management.
Each type of converter caters to a specific segment of users, reflecting the diverse needs within the market.
Comparison of Popular PDF Converters
The following table compares three popular PDF converters across key features and pricing:
| Feature | Adobe Acrobat Pro DC | Nitro PDF Pro | Smallpdf |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion Formats | Extensive (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, images, etc.) | Wide range (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, images, etc.) | Many common formats (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, images) |
| Editing Capabilities | Advanced editing, including text and image manipulation | Robust editing tools, similar to Adobe | Basic editing features; more extensive features require a paid subscription. |
| Security Features | Strong security features, including digital signatures and password protection | Good security features, including digital signatures and password protection | Basic password protection |
| Pricing | Subscription-based; relatively expensive | Subscription-based; less expensive than Adobe | Freemium model; basic features are free; advanced features require a paid subscription. |
| Platform Availability | Desktop (Windows, macOS), Mobile (iOS, Android), Web | Desktop (Windows, macOS), Mobile (iOS, Android) | Web, Mobile (iOS, Android) |
Functionality of PDF Converters
PDF converters are essential tools for anyone working with digital documents. They bridge the gap between the ubiquitous PDF format and other commonly used file types, enabling seamless collaboration and data exchange. Understanding their functionality is key to leveraging their full potential.PDF converters achieve this by employing various techniques to extract and reformat the data contained within a PDF file.
This process isn’t always straightforward, as PDFs can be structured in vastly different ways, from simple text documents to complex layouts with embedded images and sophisticated formatting.
Conversion Processes
The core function of a PDF converter is to translate the information in a PDF into another format. Converting a PDF to a Word document, for instance, involves extracting the text, formatting, and images from the PDF and then reconstructing it within the Word document’s structure. Similarly, conversion to Excel involves identifying tabular data within the PDF and importing it into a spreadsheet, and conversion to JPG involves rendering the visual content of the PDF as an image.
The complexity of the conversion depends heavily on the PDF’s structure and the target format.
Conversion Methods
Different PDF converters utilize various methods to handle the conversion process, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
OCR is crucial for converting scanned documents or image-based PDFs into editable text formats. OCR software analyzes the image of the text, recognizing the characters and converting them into machine-readable text. This allows you to edit the text once it’s in a format like Word or Excel. Think of converting an old, scanned family recipe into a digital Word document you can edit.
OCR is the key to making that possible.
Image-Based Conversion
Image-based conversion focuses on the visual representation of the PDF. The converter essentially treats the PDF as a series of images and converts it to a corresponding image format, such as JPG or PNG. This method preserves the visual layout perfectly but sacrifices the ability to edit the text content. This is ideal for situations where you need a precise visual copy of the PDF, such as archiving a visually rich presentation.
Text-Based Conversion
Text-based conversion prioritizes extracting the text content of the PDF, often neglecting the visual layout. The output will typically be a plain text file or a document with minimal formatting. This method is quick and efficient for extracting text from simple PDFs but might lead to a significant loss of formatting. Imagine converting a research paper; text-based conversion would give you the text but might lose the citations and formatting.
Formatting Loss During Conversion
It’s important to acknowledge that converting PDFs to other formats often results in some degree of formatting loss. Complex layouts, special fonts, and embedded objects may not translate perfectly to the target format. For example, converting a PDF with intricate tables and custom formatting to a Word document might result in a less visually appealing and slightly altered version of the original.
The extent of the loss depends on the complexity of the PDF, the conversion method used, and the capabilities of the converter itself.
Scenario-Specific Conversion Methods
The optimal conversion method depends heavily on the specific needs of the user and the characteristics of the PDF.For instance, OCR is best suited for scanned documents or image-based PDFs where the goal is to create an editable text version. Image-based conversion is ideal when preserving the visual layout is paramount, such as converting a visually rich marketing brochure.
Finally, text-based conversion is efficient for quickly extracting text content from simple PDFs where formatting isn’t a major concern, such as extracting text from a simple legal document for quick reference.
Seriously, PDF converters are a lifesaver, right? I mean, who hasn’t needed to change a file format at some point? Finding the right one often means checking out different kinds of software , comparing features and ease of use. Once you find a solid PDF converter though, it’s a game changer for productivity.
User Experience of PDF Converters
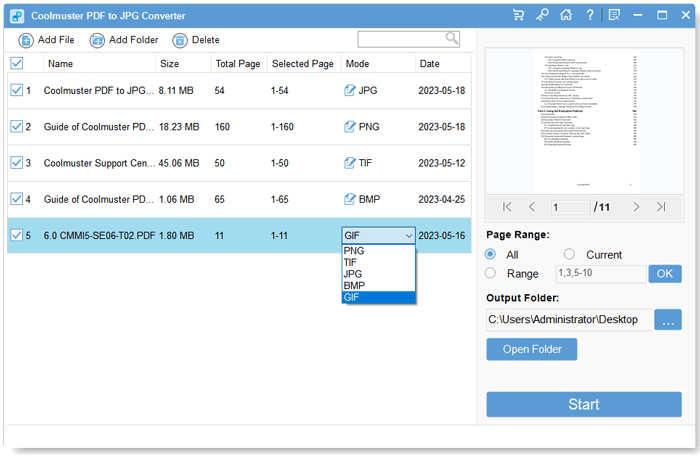
The user experience (UX) of a PDF converter significantly impacts its adoption and overall satisfaction. A clunky, confusing interface can quickly frustrate users, even if the underlying conversion technology is top-notch. Conversely, a well-designed interface can make even complex conversions feel effortless. This section explores the UX aspects of various PDF converter applications, focusing on what makes for a positive user experience.
Different PDF converter applications offer varying levels of user-friendliness. Some prioritize simplicity, providing a streamlined interface with minimal features, while others offer a broader range of tools and options, sometimes at the cost of ease of use. Popular converters often achieve a balance, incorporating powerful features while maintaining an intuitive design. This balance is key to a successful product.
Ease of Use and Intuitive Interface Design
The ease of use of a PDF converter hinges on several factors. A clear and uncluttered interface, with logically grouped options, is crucial. Intuitive icons and tooltips can significantly improve the user experience, guiding users through the process without requiring extensive instruction manuals. Popular converters like Adobe Acrobat Pro and Smallpdf, for example, generally excel in this area, providing a smooth and efficient workflow.
Smallpdf, in particular, is known for its minimalist and exceptionally user-friendly design, focusing on core functionality without overwhelming the user. In contrast, some less popular or free converters might have a more cluttered interface or less intuitive navigation.
Features Contributing to a Positive User Experience
Several features significantly enhance the user experience of PDF converters. Batch processing, allowing users to convert multiple files simultaneously, is a time-saver appreciated by all. Drag-and-drop functionality, enabling users to simply drag files from their file explorer directly into the converter, adds to the ease and speed of the process. Real-time progress indicators keep users informed about the conversion status, preventing uncertainty and frustration.
Options for customizing the output (e.g., choosing the output quality, file size, and page range) provide users with greater control and flexibility. Finally, clear error messages and helpful troubleshooting options are essential for handling any issues that may arise during the conversion process.
Improved PDF Converter User Interface Mockup
Imagine a PDF converter interface with a clean, modern design. The central area features a large drop zone with a clear “Drag and Drop Files Here” instruction. Below this, a progress bar dynamically updates as files are processed. To the right, a sidebar provides options for output settings: File type (PDF, DOCX, JPG, etc.), compression level (High, Medium, Low), and page range (All, Custom).
A simple, easily understandable “Convert” button is prominently displayed. The top navigation bar includes clear icons for “Open,” “Recent Files,” and “Settings.” The “Settings” menu allows users to customize the application’s behavior, such as default output settings and notification preferences. This design prioritizes simplicity and clarity, providing a user-friendly experience for both novice and experienced users.
The visual elements would be clean and uncluttered, employing a consistent color scheme and typography to enhance readability and overall aesthetic appeal. Error messages would be displayed prominently but in a non-intrusive manner, providing actionable steps to resolve the issue. The entire interface would be responsive, adapting seamlessly to different screen sizes and devices.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Uploading documents to online PDF converters, especially those containing sensitive information like financial records, medical data, or legal agreements, introduces inherent security risks. The process often involves transmitting data across networks, creating vulnerabilities that malicious actors could exploit. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for protecting your valuable information.
Security Implications of Uploading Sensitive Documents
The act of uploading sensitive documents to an online PDF converter inherently exposes that data to potential interception or unauthorized access. Data breaches at converter services are a real possibility, and even reputable providers can fall victim to sophisticated attacks. Furthermore, the transmission of data over the internet, even with encryption, is never entirely risk-free. The more sensitive the document, the greater the potential damage from a breach.
Consider the implications of a leaked tax return or confidential business proposal. The consequences could range from identity theft and financial loss to reputational damage and legal repercussions.
Privacy Risks Associated with Free or Less Reputable Converters
Free PDF converters often operate on a freemium model, monetizing their services through advertising or data collection. This means your uploaded documents might be subject to analysis for targeted advertising or even sold to third-party data brokers. Less reputable converters may lack robust security measures, making them easier targets for hackers. Their privacy policies might be vague or non-existent, leaving your data vulnerable to misuse.
Unlike established companies with a vested interest in protecting their reputation, these less reputable providers may offer minimal protection and lack the resources for adequate security infrastructure. The potential for data breaches and privacy violations is significantly higher.
Security Measures Employed by Different PDF Converter Providers
Reputable PDF converter providers employ various security measures to protect user data. These can include robust encryption during transmission and storage, secure server infrastructure, regular security audits, and compliance with relevant data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Some providers offer end-to-end encryption, meaning only the user and the intended recipient can access the converted document. Others might use multi-factor authentication to protect user accounts.
The level of security varies greatly between providers, however. It’s essential to research a provider’s security practices before uploading sensitive information. Look for transparency in their security policies and evidence of third-party security audits.
Best Practices for Protecting Sensitive Data When Using PDF Converters
Several best practices can mitigate the risks associated with using PDF converters. First, always choose reputable providers with strong security reputations and transparent privacy policies. Avoid using free converters from unknown sources. Second, minimize the amount of sensitive information in your documents before converting them. Remove any unnecessary personally identifiable information (PII) that is not essential to the document’s purpose.
Third, consider using a converter that offers end-to-end encryption. This provides the highest level of security by ensuring that your data is only accessible to you and your intended recipient. Finally, after conversion, promptly delete the original document and the converted PDF from your device and cloud storage to reduce the risk of exposure.
Technical Aspects of PDF Conversion
PDF conversion isn’t just about clicking a button; it’s a complex process involving sophisticated algorithms and a deep understanding of various file formats. This section delves into the technical nuts and bolts of how PDF converters work, the challenges they face, and common issues users might encounter.
Underlying Technology of PDF Conversion
PDF conversion relies on a combination of techniques, primarily involving parsing the source document’s structure and rendering it into the PDF format. For example, converting a Word document (.docx) involves extracting text, formatting information (fonts, styles, etc.), and images. This data is then restructured according to the PDF specification, which uses a complex structure of objects and streams to represent the document’s content.
This process often utilizes libraries like Ghostscript or other specialized PDF manipulation tools. Different converters might use proprietary algorithms or optimized approaches for specific file types, leading to variations in conversion quality and speed. Advanced converters might even employ machine learning to improve accuracy in handling complex layouts or images.
Supported File Formats
PDF converters typically support a wide array of input and output formats. Common input formats include Microsoft Word (.doc, .docx), Microsoft Excel (.xls, .xlsx), PowerPoint (.ppt, .pptx), text files (.txt), images (JPEG, PNG, TIFF, GIF), HTML, and various other proprietary formats. The output is most commonly PDF, but some converters also offer options for other formats like XPS, SVG, or even converting back to the original input format.
The breadth of supported formats is a key differentiator between different PDF converter software and services. For instance, a high-end converter might support obscure CAD formats, while a basic converter may only handle common office documents.
Challenges in Converting Complex PDF Documents
Converting complex PDFs presents unique challenges. Documents with intricate layouts, embedded fonts, scanned images, and digital signatures require sophisticated handling. For example, accurately preserving the formatting of a scanned document that contains tables or columns is computationally intensive. The converter needs to use Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract the text and then attempt to reconstruct the original layout, a process that can be prone to errors, especially with low-resolution scans or complex layouts.
Similarly, handling embedded fonts requires the converter to ensure these fonts are available in the output PDF or substituted with appropriate alternatives, otherwise, the output might render incorrectly. In addition, preserving digital signatures and other security features requires specialized handling to maintain the integrity and validity of the document.
Common Technical Issues and Solutions
Several technical issues can arise during PDF conversion.
- Font Rendering Issues: Incorrect font rendering can occur if the converter doesn’t have access to the original fonts. Solution: Embedding fonts in the output PDF or using a converter that handles font substitution effectively.
- Image Quality Degradation: Images can lose quality during conversion, especially with lossy compression algorithms. Solution: Using converters with high-quality image processing or selecting lossless compression options.
- Layout Problems: Complex layouts can be distorted during conversion. Solution: Choosing a converter known for its accurate layout preservation or pre-processing the document to simplify the layout.
- Data Loss: Certain data, like hyperlinks or metadata, might be lost during conversion. Solution: Using a converter that explicitly preserves metadata and hyperlinks or verifying the output for data integrity.
- Conversion Errors: Corrupted or malformed input files can lead to conversion failures. Solution: Repairing the input file or using a robust converter that can handle corrupted files.
Pricing Models of PDF Converters
So, you’re thinking about getting a PDF converter, huh? Great! But before you dive in, let’s talk about the money – specifically, how much these things cost. PDF converters employ a variety of pricing models, each with its own perks and drawbacks. Understanding these models will help you choose the best option for your needs and budget.The pricing of PDF converters is influenced by a number of factors, creating a pretty diverse market.
Features, of course, play a huge role – a basic converter offering only simple conversion will naturally be cheaper than one with advanced editing, OCR, and security features. Usage limits are another biggie; some converters might restrict the number of files you can convert per month or the size of those files. Finally, the level of support offered impacts the price – expect to pay more for dedicated customer support via phone, email, or chat.
Pricing Model Comparisons
PDF converters typically fall into three main pricing categories: free, freemium, and subscription. Free converters often have significant limitations, such as watermarks on output files or restrictions on the number of conversions. Freemium models offer a basic free version with limited features and a paid version that unlocks more functionality. Subscription models, often preferred by businesses, provide access to the full range of features for a recurring fee.
Each model caters to different needs and budgets. For example, a casual user might be perfectly happy with a free converter with limitations, while a business requiring robust features and high conversion volume would likely opt for a subscription.
Factors Influencing Pricing
As mentioned, several key factors influence the pricing of PDF converters. The number and sophistication of features directly impact the cost. Advanced features like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), batch processing, digital signature support, and advanced editing capabilities will significantly increase the price. Usage limits also play a significant role. Free or freemium versions often impose limits on file size, number of conversions, or output quality.
These limitations encourage users to upgrade to a paid version for unlimited access. Finally, the level of customer support provided affects the price. Premium converters typically offer priority support channels and more comprehensive documentation.
Pricing Tiers and Features
| Converter | Pricing Model | Key Features | Price (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smallpdf | Freemium | Basic PDF conversion, merging, splitting; Advanced features (e.g., editing, compression) require a paid subscription. | Free (limited); $6/month (Pro) |
| Adobe Acrobat Pro | Subscription | Extensive editing, OCR, digital signature support, form creation, advanced security features. | $15/month (approx.) |
| Foxit PDF Editor | Subscription/One-time Purchase | PDF creation, editing, annotation, form filling, security features; pricing varies depending on features and license type. | Varies, from $100+ for a perpetual license to subscription options |
| Nitro PDF Pro | Subscription | Similar to Adobe Acrobat Pro, offering a comprehensive suite of PDF tools. | $15/month (approx.) |
Integration with Other Applications

PDF converters aren’t just standalone tools; their real power shines when they seamlessly integrate with your existing workflow. This integration boosts productivity by streamlining document processes and minimizing manual intervention. Think of it as connecting the dots between your various applications, creating a smooth, efficient path for your documents.Effective integration with other applications dramatically improves workflow efficiency. Instead of juggling multiple programs and manually transferring files, users can convert PDFs directly within their preferred productivity suites.
This eliminates the need for tedious copy-pasting, file saving, and format conversions, saving valuable time and reducing the potential for errors. The benefits extend beyond simple time savings; it also reduces the cognitive load associated with managing multiple applications.
Integration with Microsoft Office Suite
Many PDF converters offer robust integration with Microsoft Office applications like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. This allows users to convert documents directly from within the Office suite, bypassing the need to open a separate PDF converter application. For example, a user could convert a Word document to a PDF with a single click from within the Word ribbon, maintaining the original formatting and layout.
This integration often includes features such as the ability to select the PDF conversion settings (e.g., compression level, security options) directly from the Office interface, further streamlining the process. The result is a more intuitive and user-friendly experience, making PDF conversion a seamless part of the document creation and editing process.
Integration with Google Workspace
Similar to Microsoft Office, many PDF converters integrate with Google Workspace, offering similar benefits for users working within the Google ecosystem. This integration often leverages Google Drive’s API, allowing users to convert files stored in Google Drive directly without downloading or uploading files. For example, a user might convert a Google Doc to a PDF from the Google Drive interface, choosing options such as embedding fonts or setting security restrictions.
This tight integration reduces the friction associated with using multiple platforms, enhancing productivity and collaboration within Google Workspace. The ability to automate conversion tasks via Google Apps Script further enhances efficiency for power users.
Automating PDF Conversion Tasks
Many modern PDF converters offer scripting capabilities or APIs, enabling users to automate repetitive conversion tasks. This automation is especially beneficial for organizations or individuals dealing with a high volume of PDF conversions. For instance, a company could use a script to automatically convert all incoming invoices (stored in a specific folder) to PDFs and then upload them to a cloud storage service.
This automated workflow significantly reduces manual effort and ensures consistency in the conversion process. The specific methods for automation vary depending on the PDF converter and the user’s technical expertise; some might use command-line tools, while others might leverage more advanced scripting languages or APIs. Examples of APIs commonly used include the RESTful APIs provided by many cloud-based PDF conversion services.
This allows developers to integrate PDF conversion functionality directly into their own applications.
Mobile PDF Converter Applications
Mobile PDF converter apps have become increasingly popular, offering users the convenience of converting documents on the go. This section explores the features, usability, advantages, disadvantages, and design considerations of these applications across different mobile platforms. The rapid growth of mobile device usage necessitates a thorough understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this segment of the PDF converter market.
The functionality of mobile PDF converters largely mirrors their desktop counterparts, offering core features like conversion between PDF and various other formats (like Word, Excel, and JPG). However, the mobile experience differs significantly due to limitations in processing power, screen size, and user interaction paradigms. The user experience is therefore paramount to the success of these apps.
Feature Comparison Across Platforms
Mobile PDF converter apps on iOS and Android offer similar core functionalities, such as converting PDFs to and from common formats like DOCX, XLSX, and JPG. However, there are subtle differences in the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design philosophies. iOS apps often prioritize a cleaner, more minimalist aesthetic, while Android apps might offer a wider range of customization options.
Some iOS apps might integrate more seamlessly with the Apple ecosystem, while Android apps might offer better compatibility with various cloud storage services. Ultimately, the specific features available can vary significantly depending on the individual app developer. For example, one app might offer OCR (Optical Character Recognition) while another might focus on efficient file compression. A direct comparison would require analyzing several leading apps on each platform.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile PDF Converters
The primary advantage of mobile PDF converters is their portability and convenience. Users can easily convert documents anytime, anywhere, without needing a desktop computer. This is especially beneficial for professionals who frequently work on the go or students needing to access and manipulate documents during lectures or study sessions.
- Portability and Convenience: Access and convert documents from anywhere.
- Quick Conversions: Often faster than uploading to online converters.
- Offline Functionality: Some apps allow conversion without an internet connection.
However, mobile PDF converters also have limitations. Processing power constraints on mobile devices can lead to slower conversion speeds compared to desktop applications, especially for large files. Screen size limitations can make editing or reviewing converted documents challenging. Security concerns also exist, as sensitive documents are being handled on a device that might be vulnerable to loss or theft.
- Processing Power Limitations: Slower conversion speeds for large files.
- Screen Size Limitations: Difficult to review and edit documents on smaller screens.
- Security Risks: Potential for data loss or unauthorized access.
Challenges of Optimizing PDF Converters for Mobile Devices
Optimizing PDF converters for mobile devices presents several significant challenges. Limited processing power and battery life require efficient algorithms and careful resource management. The smaller screen size necessitates intuitive UI design to avoid overwhelming the user. Maintaining compatibility across various Android and iOS versions, and different device models, adds complexity. Balancing functionality with performance is a key challenge, as features like OCR require substantial processing power.
Developers must also consider the impact of network connectivity on the user experience, ensuring seamless offline functionality where possible. Finally, security considerations must be prioritized, including data encryption and protection against malware.
Design Considerations for User-Friendly Mobile PDF Converter Apps
Designing a user-friendly mobile PDF converter app requires careful consideration of several factors. Intuitive navigation is crucial, with clear and concise menus and options. The app should be visually appealing and easy to use, even for users unfamiliar with PDF conversion software. Efficient file management features, such as easy importing and exporting from cloud storage services, are also essential.
The app should provide clear feedback to the user during the conversion process, and handle errors gracefully. Providing options for customization, such as choosing output quality and file format, allows users to tailor the conversion process to their specific needs. Finally, accessibility features should be considered to ensure the app is usable by a wide range of users.
Future Trends in PDF Conversion Technology
The world of PDF conversion is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing. We’re moving beyond simple text and image extraction to a future where PDF conversion is seamless, intelligent, and deeply integrated into our digital workflows. This section explores the emerging trends shaping this exciting field.
Several key areas are poised for significant advancements. Improved accuracy in optical character recognition (OCR), the ability to handle increasingly complex document layouts, and the integration of AI for smarter, more contextual conversion are just a few examples. These improvements will lead to a more efficient and user-friendly experience for everyone who works with PDFs.
AI-Powered Conversion and Enhanced OCR Accuracy
AI is revolutionizing PDF conversion. Current OCR technology struggles with complex layouts, handwritten text, and low-quality scans. However, advancements in deep learning are enabling more accurate and robust OCR, capable of handling even the most challenging documents. For example, AI-powered systems can now learn to identify different handwriting styles and even decipher text from blurry or damaged images with a significantly higher degree of accuracy than older methods.
This translates to less manual intervention, faster processing times, and a higher quality end product. Future iterations might even incorporate contextual understanding, correctly identifying tables, figures, and other elements within the document to improve overall accuracy and organization.
Improved Handling of Complex Document Layouts
Many PDFs are not simple text documents; they contain intricate layouts with columns, tables, images, and embedded fonts. Traditional conversion methods often struggle to maintain the original formatting during conversion. However, future PDF converters will likely leverage AI and machine learning to intelligently analyze and preserve the complex layout structure during the conversion process. Imagine a system that automatically recognizes columns and tables, preserving their structure and formatting in the output file, regardless of the target format.
This would greatly improve the fidelity of the converted document and eliminate the need for extensive manual reformatting.
Predictive Conversion and Automated Document Processing, Pdf converter
Looking further ahead, we can envision PDF converters that predict the user’s needs and automatically select the optimal conversion settings. For instance, a converter might detect that a document is a scientific paper and automatically apply settings that preserve mathematical formulas and specialized symbols. This level of automation would significantly streamline document workflows, freeing users from the burden of manually configuring conversion settings.
Moreover, these systems could be integrated with other applications, automating the entire document processing pipeline from ingestion to archiving. Think of an automated system that receives a scanned invoice, automatically extracts key information, and updates accounting software—all without any human intervention.
Timeline of Anticipated Advancements
Predicting the exact timeline for these advancements is challenging, but we can anticipate a phased rollout. We’ve already seen significant improvements in OCR accuracy and AI-powered layout analysis in the last few years. Within the next 3-5 years, we expect to see widespread adoption of AI-powered conversion features in mainstream PDF converters. Within the next 5-10 years, predictive conversion and automated document processing capabilities are likely to become more prevalent, transforming how we interact with PDFs.
Beyond 10 years, the line between PDF conversion and other document processing tasks may blur, with highly sophisticated systems capable of automatically understanding, organizing, and even summarizing large collections of PDF documents.
Case Studies of PDF Converter Usage
PDF converters are ubiquitous tools impacting various sectors. Their application spans from streamlining everyday tasks to solving complex organizational challenges across diverse industries. Examining real-world examples showcases the versatility and impact of these tools. The following case studies highlight the benefits and demonstrate how PDF converters are transforming workflows.
PDF Converter Use in Education
Educational institutions rely heavily on document management. Professors distribute syllabi, assignments, and readings; students submit papers and projects. A robust PDF converter allows for seamless conversion between various file formats (like Word docs, presentations, images) and the universally accepted PDF format. This ensures compatibility across different operating systems and devices, improving accessibility for both instructors and students. For example, a university might use a converter to batch-convert scanned exam papers into searchable PDFs for easier grading and archiving.
This saves significant time and improves the overall efficiency of the grading process.
PDF Converter Applications in Business
Businesses leverage PDF converters for a multitude of purposes, from creating visually appealing marketing materials to securing sensitive client data. Sales teams might use converters to transform presentations into easily shareable PDFs, while legal departments might use them to manage and archive contracts in a secure and accessible format. Consider a large corporation that uses a converter to automate the process of converting invoices from various sources into a standardized PDF format.
This automation streamlines accounting processes and reduces the risk of errors. Further, the ability to add digital signatures to PDFs improves the security and authenticity of crucial business documents.
PDF Converter Usage in Government
Government agencies handle massive volumes of documents, many of which require secure and reliable storage and sharing. PDF converters play a vital role in this process, ensuring the integrity and accessibility of official records. For instance, a government agency might use a converter to create accessible PDFs of public documents, ensuring compliance with accessibility regulations. This enhances transparency and ensures equal access to information for citizens with disabilities.
Another example involves converting physical records to digital PDFs for easier archiving and retrieval, reducing storage space and improving efficiency.
Case Study Table: PDF Converter Success Stories
| Application | Challenges Addressed | Results Achieved | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Converting scanned historical documents to searchable PDFs | Inefficient manual data entry, difficulty in accessing information | Improved access to historical data, reduced data entry costs, increased research efficiency | Government Archives |
| Creating accessible course materials for students with disabilities | Incompatibility of file formats, difficulty in accessing information for students with visual impairments | Improved accessibility for students, compliance with accessibility regulations | Higher Education |
| Automating invoice processing through PDF conversion | Manual data entry errors, slow processing times | Reduced processing time, improved accuracy, reduced operational costs | Finance |
| Creating secure and shareable client contracts | Difficulty in sharing and managing contracts, risk of unauthorized access | Improved security, streamlined contract management, enhanced client communication | Legal Services |
Accessibility Features in PDF Converters
Making PDFs accessible is super important for everyone, but especially for people with disabilities. A good PDF converter should help create documents that are usable by those with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. Without proper accessibility features, a PDF can be essentially unusable for a significant portion of the population, creating a barrier to information and communication.
Essential Accessibility Features
Several key features are crucial for ensuring PDF accessibility. These features make it possible for assistive technologies, such as screen readers, to accurately interpret and convey the content of the PDF to users. Without these features, a visually impaired person using a screen reader might only hear a jumbled mess of text and image descriptions, rendering the document useless.
Support for screen readers is paramount, allowing users to navigate the document linearly, access headings, and understand the structure. Alt text for images provides textual descriptions, conveying the meaning and context of images to those who cannot see them. Proper use of headings (H1, H2, etc.) establishes a logical document structure, allowing screen readers to easily navigate and summarize the content.
Furthermore, color contrast should be sufficient to ensure readability for users with low vision, and the use of tables should be structured semantically to aid understanding. Finally, clear and consistent language helps ensure that the document is easy to understand for everyone.
Accessibility Feature Comparison Across PDF Converters
Different PDF converters offer varying levels of accessibility support. For example, Adobe Acrobat Pro, a widely used professional tool, provides extensive accessibility features, including tools to check for accessibility issues and automatically add alt text to images based on OCR (Optical Character Recognition). However, it comes with a hefty price tag. Free and open-source converters, like LibreOffice Draw, offer some accessibility features but might lack the advanced capabilities and automated checks of commercial software.
Online converters often have limited accessibility features, primarily focusing on basic conversion functionalities. The level of accessibility support should be a major factor when choosing a PDF converter, particularly if you need to create accessible documents regularly. A direct comparison of features across several popular converters (Adobe Acrobat Pro, LibreOffice Draw, Smallpdf, Nitro PDF Pro) would reveal significant variations in capabilities and user experience.
Recommendations for Improving Accessibility in PDF Converter Software
To improve the accessibility of PDF converters, several recommendations can be made. First, developers should prioritize the integration of robust accessibility checkers that go beyond basic compliance checks. These checkers should identify potential accessibility problems, such as missing alt text or low color contrast, and provide clear guidance on how to fix them. Secondly, improvements to automated alt text generation are needed.
Current OCR technology isn’t always perfect; therefore, more advanced AI-powered solutions that can accurately interpret images and generate relevant alt text are crucial. Thirdly, developers should provide clear and user-friendly instructions on how to create accessible PDFs within their software. This includes tutorials and examples that demonstrate best practices. Finally, regular updates and improvements to accessibility features should be a priority to keep pace with evolving accessibility standards and technologies.
Consider the case of a large university adopting a new PDF converter; ensuring that the software meets accessibility standards will allow students with disabilities to access crucial course materials, ultimately enhancing their educational experience.
Final Review
So, there you have it – a comprehensive look at the world of PDF converters! From the market overview and the technical aspects to user experience and future trends, we’ve covered a lot of ground. Hopefully, you now have a much clearer understanding of how these tools work, their strengths and weaknesses, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Whether you’re a student juggling assignments, a professional managing documents, or just someone who needs to convert a PDF every now and then, mastering PDF conversion can seriously streamline your workflow. Go forth and convert!
General Inquiries: Pdf Converter
What’s the difference between OCR and image-based conversion?
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) converts scanned images of text into editable text. Image-based conversion simply converts the image to another format, keeping it as a picture, not editable text.
Can I convert a password-protected PDF?
It depends on the converter and the type of password protection. Some converters can handle simple passwords, while others can’t handle encryption. You might need to remove the password first.
Are online PDF converters safe for sensitive documents?
Use caution. While some reputable services offer encryption, uploading sensitive documents to online converters carries inherent risks. For highly confidential files, consider desktop converters or those with robust security features.
What if my conversion fails?
Try a different converter or conversion method. Complex PDFs might require more powerful software. Check the file for corruption or errors.
How can I batch convert multiple PDFs?
Most converters offer a batch processing feature. Look for options like “add files,” “select folder,” or similar functionalities to convert multiple PDFs simultaneously.
