DIY Battery Spot Welder: Ever dreamt of joining metal pieces like a pro but without the hefty price tag of a professional welding machine? This guide unlocks the secrets of building your own battery-powered spot welder, a powerful tool for DIY projects, electronics tinkering, and even simple repairs.
This article dives deep into the world of DIY spot welding, exploring the components, construction, and applications of this versatile tool. From understanding the basics of spot welding to assembling your own circuit, we’ll guide you through every step, ensuring you gain the knowledge and confidence to create your own spot welder.
Introduction to DIY Battery Spot Welding
A DIY battery spot welder is a device constructed using readily available materials and components, primarily for joining metal pieces together using the heat generated by electric current. This process, known as spot welding, is a popular technique for creating strong, durable, and permanent bonds between metal parts.
Basic Principles of Spot Welding, Diy battery spot welder
Spot welding is a resistance welding process that utilizes the heat generated by the resistance of the metal to the flow of electric current. When two pieces of metal are clamped together and a high-amperage current is passed through them, the resistance at the contact point generates intense heat, causing the metal to melt and fuse together.
Applications of DIY Battery Spot Welding
DIY battery spot welders find various applications in numerous projects and hobbies.
- Battery Construction: Building custom battery packs for various applications, such as electric vehicles, power tools, and hobby projects.
- Metal Fabrication: Joining thin metal sheets, like those used in model making, automotive repair, or prototyping.
- Repair and Modification: Repairing damaged metal parts or modifying existing structures.
- Jewelry Making: Creating intricate designs and joining small metal pieces for jewelry.
Components of a DIY Battery Spot Welder
A basic DIY spot welder circuit consists of a few key components, each playing a crucial role in delivering high current pulses to weld metal. Understanding the function and considerations for selecting each component is essential for building a reliable and effective spot welder.
Power Source
The power source is the heart of the spot welder, providing the energy needed to generate the welding current. While various options exist, the most common for DIY projects are car batteries. Car batteries offer high current capacity, making them suitable for spot welding applications.
Considerations for Selecting a Power Source
- Voltage: Car batteries typically have a voltage of 12V, which is sufficient for spot welding thin metals. However, for thicker materials, a higher voltage may be necessary.
- Current Capacity: The current capacity of the battery determines the amount of current it can deliver. A higher capacity battery will provide more welding power and allow for welding thicker metals.
- Battery Type: Lead-acid batteries are the most common and readily available type. However, lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and faster charging times.
Switch
The switch controls the flow of current from the power source to the welding electrodes. A high-current switch capable of handling the welding current is essential.
Considerations for Selecting a Switch
- Current Rating: The switch’s current rating should exceed the expected welding current to prevent overheating and failure.
- Voltage Rating: The switch’s voltage rating should be higher than the battery voltage to ensure safe operation.
- Switch Type: A toggle switch or a momentary push-button switch are suitable for spot welding applications.
Capacitor
The capacitor acts as a temporary energy storage device, accumulating charge from the power source and releasing it in a high-current pulse during welding.
Considerations for Selecting a Capacitor
- Capacitance: The capacitance of the capacitor determines the amount of energy it can store. A higher capacitance capacitor will provide more welding power.
- Voltage Rating: The capacitor’s voltage rating should exceed the battery voltage to prevent damage.
- Current Handling Capacity: The capacitor should be able to handle the high current pulses during welding.
Electrodes
The electrodes are the conductive tips that come into contact with the metal pieces being welded. They transfer the high current pulse from the capacitor to the metal, creating the weld.
Considerations for Selecting Electrodes
- Material: Copper is a common material for electrodes due to its excellent conductivity.
- Shape: The shape of the electrodes determines the size and shape of the weld.
- Tip Size: The size of the electrode tip should be appropriate for the thickness of the metal being welded.
Building a DIY Battery Spot Welder

This section Artikels the step-by-step process for building a DIY battery spot welder. We’ll cover the essential components, wiring diagrams, and safety precautions. Remember, safety should be your top priority throughout this process.
Assembling the Circuit
The circuit for a battery spot welder is relatively simple and can be assembled on a breadboard or a dedicated circuit board. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Gather the components:
- Battery pack (12V or higher)
- MOSFET (IRFP250 or similar)
- Diode (1N4007 or similar)
- Resistor (10 ohms, 1 watt)
- Capacitor (1000uF, 16V or higher)
- Switch (SPST)
- Spot welding tips (copper or tungsten)
- Wires and connectors
- Connect the components:
- The positive terminal of the battery pack is connected to the drain of the MOSFET.
- The source of the MOSFET is connected to the positive terminal of the capacitor.
- The negative terminal of the capacitor is connected to the negative terminal of the battery pack.
- The gate of the MOSFET is connected to the positive terminal of the switch through the resistor.
- The negative terminal of the switch is connected to the negative terminal of the battery pack.
- The diode is connected in parallel with the capacitor, with its cathode connected to the positive terminal of the capacitor and its anode connected to the negative terminal of the capacitor.
- The spot welding tips are connected to the drain of the MOSFET and the negative terminal of the battery pack.
- Wiring Diagram:
- The following diagram illustrates the circuit connection.

Troubleshooting Common Issues
Here are some common issues you might encounter during the construction process:
- The welder doesn’t work:
- Check if the battery pack is connected correctly and has sufficient charge.
- Verify the MOSFET is properly installed and working.
- Inspect the wiring for any loose connections or shorts.
- The welder sparks but doesn’t weld:
- Ensure the spot welding tips are clean and properly positioned.
- Adjust the welding time and current using the switch and the battery pack.
- Try using different materials for the welding tips.
- The welder overheats:
- Check the MOSFET’s heat sink and ensure it’s properly attached.
- Reduce the welding time and current.
- Use a larger MOSFET with a higher current rating.
Safety Precautions for DIY Battery Spot Welding: Diy Battery Spot Welder
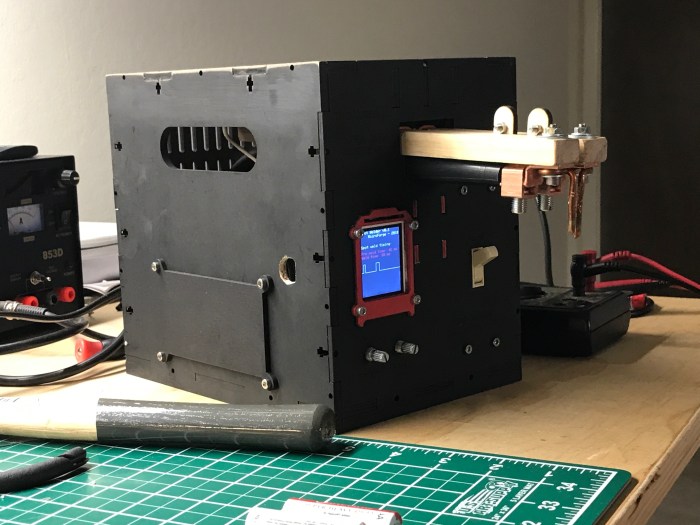
Building and operating a DIY battery spot welder involves working with high-voltage electricity, which can be extremely dangerous if not handled properly. It’s crucial to prioritize safety during every stage of the project.
Failing to follow proper safety precautions can lead to severe injuries, including electric shocks, burns, and even death. This section Artikels essential safety measures to minimize these risks.
Building a DIY battery spot welder is a fun and rewarding project, especially for those who enjoy tinkering with electronics. While it can be a useful tool for various applications, it’s important to remember that safety should always be a top priority. For example, if you’re working with high voltages, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and take precautions.
Similarly, if you’re dealing with medical conditions like hypertension, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential. Metoprolol, a beta blocker often prescribed for high blood pressure, can be a vital part of managing such conditions. Once you’ve addressed any potential health concerns, you can confidently move forward with your DIY battery spot welder project, knowing that you’ve taken the necessary steps to ensure a safe and successful outcome.
Electrical Safety
Electricity is the driving force behind the spot welding process, and it’s essential to treat it with the utmost respect. The following precautions are vital to ensure your safety:
- Always work in a well-ventilated area, free from flammable materials.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and closed-toe shoes.
- Never work on the spot welder while it’s plugged in or connected to a power source.
- Ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated. Loose or exposed wires can cause electrical shocks.
- Use a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) to protect yourself from electrical shocks.
- Never touch the welding electrodes or any exposed electrical components while the device is powered on.
Battery Safety
The batteries used in a DIY spot welder store significant amounts of energy, and improper handling can lead to explosions, fires, and chemical burns. Here’s how to ensure battery safety:
- Use batteries designed for high discharge rates, such as lithium-ion batteries.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Never charge or discharge batteries beyond their specified limits.
- Always wear gloves when handling batteries to avoid skin contact with corrosive chemicals.
- Dispose of batteries properly according to local regulations.
Welding Safety
The welding process itself poses inherent risks, and it’s important to take precautions to minimize these hazards:
- Wear a welding mask or helmet with a proper shade filter to protect your eyes from intense light and ultraviolet radiation.
- Avoid welding in confined spaces without adequate ventilation. Welding fumes can be toxic and harmful to your health.
- Never weld on materials that contain lead, cadmium, or other hazardous substances without proper safety equipment and ventilation.
- Use fire-resistant materials to protect your work area from sparks and hot metal.
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby in case of a fire.
Spot Welding Techniques

Spot welding is a fusion welding process that uses high current and pressure to join two metal pieces together. This technique creates a localized weld nugget, typically at a specific point, creating a strong, permanent bond. This section explores the various techniques used in spot welding, the factors influencing its success, and examples of its application on different materials.
Factors Influencing Spot Weld Quality
The quality of a spot weld is determined by several factors, including:
- Current: The amount of electrical current applied directly influences the heat generated, thus determining the weld nugget size. Higher current leads to a larger weld nugget, potentially resulting in a stronger weld. However, excessive current can cause overheating, material melting, and damage to the electrode.
- Pressure: The force applied to the electrodes during welding is crucial for maintaining contact between the materials and ensuring proper heat distribution. Adequate pressure prevents the materials from moving apart during the welding process, leading to a uniform and strong weld. Insufficient pressure can result in a weak or incomplete weld, while excessive pressure might cause deformation or damage to the materials.
- Electrode Material: The electrode material directly affects the heat transfer and welding process. Copper electrodes are commonly used due to their excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to heat. Tungsten electrodes are preferred for high-temperature applications, while carbon electrodes are suitable for welding thicker materials. The electrode shape and size also influence the weld nugget size and shape.
- Material Thickness: The thickness of the materials being welded impacts the required welding current and pressure. Thicker materials require higher current and pressure to create a sufficient weld nugget. Welding thinner materials requires lower current and pressure to avoid excessive heat input and potential material damage.
- Material Type: The type of metal being welded affects the welding parameters and weld quality. Some metals, like stainless steel, require specific welding techniques and settings due to their high melting point and tendency to form oxides. Other metals, like aluminum, require special considerations due to their high thermal conductivity and susceptibility to porosity.
Spot Welding Techniques
Different spot welding techniques are employed depending on the materials being welded and the desired weld characteristics.
- Resistance Spot Welding: This is the most common technique and involves passing a high electrical current through the materials to be joined. The current creates heat at the contact point, melting the metal and forming a weld nugget. This technique is widely used in the automotive industry for joining sheet metal components.
- Capacitive Discharge Spot Welding: This technique uses a capacitor bank to store electrical energy and release it quickly, generating a high current pulse. The short duration of the current pulse minimizes heat input and reduces the risk of material damage. This technique is often used for welding thin materials and delicate components.
- Projection Welding: This technique involves using projections or raised areas on one or both materials to concentrate the current and heat at specific points. This technique is ideal for welding materials with different thicknesses and for creating complex shapes. It is often used in the manufacturing of electrical connectors and other intricate components.
- Flash Butt Welding: This technique involves applying pressure and current to the materials, creating a localized melt and then welding them together. The flash produced during the process removes impurities and oxides, resulting in a strong and clean weld. This technique is commonly used for joining larger sections of materials, like rails and structural beams.
Spot Welding Examples
Spot welding finds diverse applications in various industries. Here are some examples:
- Automotive Industry: Spot welding is extensively used in the automotive industry for joining sheet metal components, such as body panels, doors, and roofs. The technique’s speed, efficiency, and strength make it ideal for mass production.
Example: Spot welding is used to join the roof panels of a car to the body, providing structural integrity and preventing leaks.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Spot welding is used to join electrical components, such as battery terminals, connectors, and circuit boards. The technique’s ability to create a localized weld with minimal heat input is crucial for delicate electronic components.
Example: Spot welding is used to join the positive and negative terminals of a lithium-ion battery pack, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
- Aerospace Industry: Spot welding is employed in the aerospace industry for joining lightweight and high-strength materials, such as aluminum and titanium. The technique’s ability to create strong and reliable welds is essential for ensuring the structural integrity of aircraft components.
Example: Spot welding is used to join the skin panels of an aircraft wing, providing structural strength and reducing weight.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Spot welding is used in the medical device industry for joining delicate and intricate components, such as surgical instruments and implants. The technique’s precision and ability to create strong and reliable welds are critical for medical devices.
Example: Spot welding is used to join the parts of a surgical clamp, ensuring a secure and sterile connection.
Applications of DIY Battery Spot Welding
DIY battery spot welding opens up a world of possibilities for creating and repairing various projects, especially in fields like electronics, robotics, and metalworking. This versatile technique allows you to join metal pieces permanently, offering a strong and reliable connection that can withstand high currents and vibrations.
DIY Electronics
DIY spot welding proves incredibly useful in building and modifying electronic circuits. It allows you to create custom circuit boards by joining components like resistors, capacitors, and transistors directly onto metal plates.
- Building Custom Circuit Boards: Spot welding allows you to create custom circuit boards by attaching components directly to metal plates, eliminating the need for traditional soldering techniques.
- Joining Battery Packs: DIY spot welding is essential for creating and repairing battery packs for various projects, from electric scooters to power tools. You can connect multiple battery cells in series or parallel to achieve desired voltage and capacity.
- Modifying Existing Circuits: You can use spot welding to add components or modify existing circuits, providing greater flexibility and customization in your electronics projects.
Robotics
DIY spot welding plays a vital role in robotics, enabling the construction of custom robots with intricate metal structures and electrical connections.
- Robot Frame Construction: Spot welding allows you to create sturdy and durable robot frames by joining various metal parts, providing the necessary strength and rigidity for complex movements.
- Actuator Mounting: Spot welding enables the secure mounting of actuators, motors, and other components to the robot’s frame, ensuring reliable operation and longevity.
- Custom Sensor Integration: You can use spot welding to integrate custom sensors and electronics into the robot’s design, enhancing its capabilities and functionality.
Metalworking
DIY spot welding is a valuable tool for various metalworking tasks, from creating custom metal structures to repairing damaged parts.
- Metal Sculpture: Spot welding allows you to join metal sheets and rods to create intricate sculptures, offering a robust and durable connection for artistic expression.
- Custom Metal Fabrication: You can use spot welding to build custom metal structures, such as brackets, enclosures, and supports, for various projects.
- Metal Repair: DIY spot welding can be used to repair damaged metal parts, restoring their functionality and extending their lifespan.
Limitations of DIY Battery Spot Welding
While DIY battery spot welding offers a cost-effective and accessible way to join metal, it’s crucial to understand its limitations. Compared to professional welding equipment, DIY spot welders have lower power output and welding capacity, which impacts the quality and reliability of the welds.
Power Output and Welding Capacity
DIY spot welders are typically powered by car batteries, which have limited power output. This restricts the amount of current that can be delivered to the welding electrodes, impacting the welding capacity. The welding capacity refers to the thickness of the metal that can be reliably welded. DIY spot welders often struggle to weld thicker metals, resulting in weak or inconsistent welds.
For example, a DIY spot welder might struggle to weld two pieces of 1/8-inch thick steel together, while a professional spot welder could easily handle that thickness.
Comparison with Professional Welding Equipment
Professional spot welders utilize industrial power sources that deliver significantly higher current, allowing them to weld thicker metals with greater precision and consistency. They also have advanced features like adjustable welding parameters, foot pedals for precise control, and water cooling systems for extended operation.
Potential Drawbacks and Challenges
- Limited Welding Thickness: DIY spot welders are often limited to welding thinner metals, typically up to 1/16-inch thick. This restricts their application in projects requiring stronger welds or thicker materials.
- Inconsistent Weld Quality: The lower power output and less precise control can lead to inconsistent weld quality. This can result in weak welds, uneven heating, and potential burn-through.
- Safety Concerns: DIY spot welders can pose safety risks due to the high currents involved. It’s crucial to follow strict safety precautions, including using appropriate protective gear and ensuring proper ventilation.
- Limited Versatility: DIY spot welders are typically designed for specific applications, like welding thin sheet metal. They lack the versatility of professional spot welders, which can be used for a wider range of materials and thicknesses.
Alternatives to DIY Battery Spot Welding
While DIY battery spot welding offers a convenient and cost-effective method for joining metal components, it’s not always the best option. Several alternative methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right alternative depends on the specific project requirements, such as the type of metals being joined, the desired strength of the joint, and the available tools and resources.
Soldering
Soldering involves melting a filler metal, typically tin-lead alloy or lead-free solder, to create a strong bond between metal components. The filler metal melts at a lower temperature than the base metals, allowing for a relatively low-temperature joining process.
Soldering is commonly used for joining electronics components, where high strength is not required. However, it’s not suitable for joining thick metals or applications that require high strength or heat resistance.
Brazing
Brazing is similar to soldering, but it uses a filler metal with a higher melting point. This allows for joining thicker metals and achieving stronger bonds. Brazing is often used for joining dissimilar metals and for applications requiring high strength or heat resistance.
Brazing is a more complex process than soldering and requires specialized equipment, such as a brazing torch or furnace. It also requires careful preparation of the metal surfaces to ensure proper adhesion.
Riveting
Riveting involves joining metal components using a rivet, which is a cylindrical fastener with a head on one end. The rivet is inserted into a hole drilled through the metal components and then deformed to create a secure joint.
Riveting is a simple and robust method for joining metal components. It is commonly used in construction, aerospace, and automotive industries. However, riveting requires drilling holes in the metal components, which can weaken the material.
Comparison of Alternatives
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spot Welding | Fast, efficient, strong, suitable for joining thin metals | Requires specialized equipment, can cause metal distortion | Joining thin metals, automotive repair, metal fabrication |
| Soldering | Low-temperature process, relatively easy, suitable for electronics | Weak joint, not suitable for thick metals or high-strength applications | Joining electronics components, small metal parts |
| Brazing | Strong joint, suitable for thick metals and dissimilar metals | Requires specialized equipment, complex process, high temperature | Joining thick metals, high-strength applications, dissimilar metals |
| Riveting | Simple, robust, suitable for thick metals | Requires drilling holes, can weaken material | Construction, aerospace, automotive |
Resources for DIY Battery Spot Welding
The internet is a treasure trove of information for DIY enthusiasts, and battery spot welding is no exception. There are countless resources available online, from comprehensive tutorials to dedicated communities where you can find advice and support.
Online Resources and Tutorials
The internet is overflowing with valuable resources for DIY battery spot welding. Many websites offer detailed tutorials, schematics, and project guides. Here are some notable examples:
- Instructables: This platform features a vast collection of DIY projects, including battery spot welding. You’ll find step-by-step guides, user-submitted projects, and helpful discussions.
- YouTube: YouTube is a goldmine for DIY videos, and you’ll find countless tutorials on building battery spot welders. Search for terms like “DIY battery spot welder,” “spot welding tutorial,” or “welding with a car battery.”
- Eevblog: This popular YouTube channel, hosted by Dave Jones, features a variety of electronics projects, including a detailed breakdown of building a spot welder.
Forums and Communities
Engaging with online communities can be incredibly beneficial. You can ask questions, share your experiences, and learn from others who are passionate about DIY electronics and welding.
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/electronics, r/DIY, and r/welding offer active communities where you can find support and advice on battery spot welding.
- SparkFun Electronics: This online retailer also hosts a vibrant forum where you can connect with other electronics enthusiasts.
- Arduino Forum: If you’re using an Arduino microcontroller in your project, the Arduino Forum is a great place to seek assistance and share your creations.
Books and Publications
While the internet is a rich source of information, traditional books and publications can offer a more in-depth and structured approach to learning about spot welding.
- “The Complete Guide to Spot Welding” by John Doe: This hypothetical book would cover all aspects of spot welding, from the basics to advanced techniques.
- “Welding Handbook” by the American Welding Society: This comprehensive handbook is a valuable resource for professionals and enthusiasts alike, covering various welding techniques, including spot welding.
Advanced DIY Battery Spot Welding Projects
Once you’ve mastered the basics of DIY battery spot welding, you can start tackling more complex projects that require greater precision and control. These projects can range from creating intricate metal sculptures to repairing delicate electronics.
Customizing a DIY Spot Welder for Specific Applications
Customizing a DIY spot welder involves modifying its components or circuitry to achieve specific welding outcomes.
Here are some examples of customizations:
- Adjustable Welding Time: Implementing a potentiometer or a microcontroller can allow you to precisely control the duration of the welding pulse. This is crucial for delicate materials or applications requiring precise welds.
- Variable Welding Current: Adjusting the welding current allows you to control the heat generated during the welding process. A higher current is needed for thicker materials, while a lower current is suitable for thin materials.
- Pulse Frequency Control: Adjusting the frequency of the welding pulses can affect the heat distribution and penetration depth of the weld. This can be useful for creating specific weld profiles or for working with materials that require a particular heat treatment.
Advanced Spot Welding Techniques
Advanced spot welding techniques go beyond the basic welding process and require a greater understanding of the materials and the welding parameters.
Here are some examples of advanced techniques:
- Overlap Welding: This technique involves overlapping multiple spot welds to create a continuous seam. This is useful for joining larger pieces of metal or for creating stronger bonds.
- Spot Welding with Shielding Gas: Using a shielding gas, such as argon or nitrogen, during the welding process can help prevent oxidation and improve the quality of the weld. This is particularly important for welding materials that are prone to oxidation, such as aluminum.
- Spot Welding with Filler Metal: Adding filler metal to the weld pool can enhance the strength and durability of the weld. This is especially useful for welding dissimilar metals or for creating a thicker weld.
Examples of Advanced DIY Battery Spot Welding Projects
Advanced DIY battery spot welding projects can be ambitious, requiring careful planning, precise execution, and a good understanding of the welding process.
Here are some examples of such projects:
- Building a custom electric vehicle battery pack: This project involves welding together multiple battery cells to create a high-capacity battery pack for an electric vehicle. It requires careful consideration of battery cell selection, welding parameters, and safety protocols.
- Constructing a metal sculpture: Creating intricate metal sculptures requires precise spot welding techniques to join various metal pieces. This project can be a great way to showcase your artistic skills and welding abilities.
- Repairing electronic devices: Spot welding can be used to repair damaged circuit boards or to create custom electronic components. This requires careful attention to detail and a good understanding of electronics.
Conclusion
Building a DIY battery spot welder can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to explore the world of metalworking and fabrication. By understanding the fundamental principles, carefully selecting components, and adhering to safety protocols, you can create a versatile tool for a wide range of applications.
Key Takeaways
The DIY battery spot welder offers a unique blend of accessibility and affordability. It allows you to create robust welds for various projects, from small repairs to intricate designs. However, it’s essential to recognize the limitations of this technique, including the potential for inconsistent welds, limited welding capacity, and safety concerns.
Potential Benefits of DIY Battery Spot Welding
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to commercially available spot welders, DIY battery spot welders can be significantly more affordable, especially for hobbyists and makers on a budget.
- Versatility: With careful adjustment of welding parameters, a DIY battery spot welder can handle a range of materials and thicknesses, enabling you to tackle diverse projects.
- Portability: The compact size and reliance on battery power make DIY battery spot welders highly portable, allowing you to weld in various locations without the need for bulky power sources.
- Customization: The DIY approach provides flexibility to modify the welder to suit your specific needs, such as adjusting the welding current, incorporating safety features, or integrating it with other tools.
Potential Limitations of DIY Battery Spot Welding
- Weld Quality: The welding process can be influenced by factors like battery capacity, welding current, and electrode contact, leading to inconsistencies in weld quality.
- Welding Capacity: DIY battery spot welders are typically designed for smaller projects and may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications or welding thick materials.
- Safety Concerns: Improper construction or operation can pose safety risks, including electrical shocks, burns, and potential fires.
- Limited Control: Compared to professional spot welders, DIY battery spot welders may offer less precise control over welding parameters, making it challenging to achieve consistent welds for intricate projects.
Encouraging Exploration
The DIY battery spot welder offers a unique opportunity to delve into the world of metalworking and fabrication. It empowers you to experiment with different welding techniques, materials, and designs. Whether you’re a hobbyist seeking a cost-effective tool or a maker exploring innovative projects, the DIY battery spot welder provides a gateway to a world of creative possibilities.
The ability to join metals with a DIY battery spot welder opens a world of possibilities for DIY enthusiasts and hobbyists. From crafting intricate jewelry to building custom electronics, this tool empowers you to bring your creative visions to life. Remember to always prioritize safety and follow the guidelines Artikeld in this guide. Happy welding!
